1. 鏈表結(jié)構(gòu)介紹
在前面章節(jié)已經(jīng)學(xué)習(xí)了數(shù)組的使用,數(shù)組的空間是連續(xù)空間,數(shù)組的大小恒定的,在很多動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)存儲的應(yīng)用場景下,使用不方便;而這篇文章介紹的鏈表結(jié)構(gòu),支持動態(tài)增加節(jié)點(diǎn),釋放節(jié)點(diǎn),比較適合存儲動態(tài)數(shù)據(jù)的應(yīng)用場景,而且鏈表的空間是存儲在堆上面的,可以動態(tài)分配,釋放。從效率上來講,數(shù)組的空間是連續(xù)的,查詢、讀取數(shù)據(jù)數(shù)組占優(yōu)勢;鏈表的優(yōu)勢在于節(jié)點(diǎn)可以動態(tài)增加、動態(tài)刪除,刪除支持任意位置的節(jié)點(diǎn)刪除。
特點(diǎn):
數(shù)組的空間是連續(xù)的,可以直接通過[]下標(biāo)訪問。
鏈表的節(jié)點(diǎn)是不連續(xù)的,需要通過每個節(jié)點(diǎn)的指針,來找到上一個節(jié)點(diǎn)或者下一個節(jié)點(diǎn)的地址。
鏈表的每個節(jié)點(diǎn)就是一個結(jié)構(gòu)體變量,節(jié)點(diǎn)里有一個或者兩個指針,可以保存上一個節(jié)點(diǎn)和下一個節(jié)點(diǎn)的地址,方便遍歷鏈表,刪除、插入節(jié)點(diǎn)時定位位置。
2. 案例: 單向鏈表的創(chuàng)建與使用
下面例子采用函數(shù)封裝的形式編寫,每個功能都使用子函數(shù)實現(xiàn)。
實現(xiàn)的功能如下:
- 初始化鏈表頭
- 插入節(jié)點(diǎn)的函數(shù)(鏈表任意位置插入,鏈表尾插入)
- 刪除節(jié)點(diǎn)的函數(shù)(鏈表任意位置刪除、鏈表尾刪除)
- 遍歷鏈表,輸出鏈表里的所有信息
#include
#include
?
//定義鏈表節(jié)點(diǎn)的結(jié)構(gòu)體
struct app
{
int a;
struct app *next; //能保存結(jié)構(gòu)體的地址
};
?
struct app *list_head=NULL; //鏈表的頭指針
?
void list_print(struct app *head);
struct app *list_HeadInit(struct app *head);
void list_add(int a,struct app *head);
void list_del(int a,struct app *head);
?
int main()
{
//1. 初始化鏈表頭
list_head=list_HeadInit(list_head);
//2. 在鏈表尾插入數(shù)據(jù)
list_add(10,list_head);
list_add(11,list_head);
list_add(12,list_head);
list_add(13,list_head);
//3. 刪除節(jié)點(diǎn)
list_del(11,list_head);
//4. 輸出鏈接節(jié)點(diǎn)里的數(shù)據(jù)
list_print(list_head);
return 0;
}
?
/*
函數(shù)功能: 初始化鏈表頭--給鏈表頭申請空間
*/
struct app *list_HeadInit(struct app *head)
{
if(head==NULL) //沒有空間
{
//1. 申請鏈表頭空間
head=malloc(sizeof(struct app));
//2. 初始化鏈表頭
head->next=NULL;
}
return head;
}
?
/*
函數(shù)功能: 在鏈表尾插入數(shù)據(jù)
int a 插入的數(shù)據(jù)值
struct app *head 鏈表頭
*/
void list_add(int a,struct app *head)
{
struct app *new_p=NULL;
struct app *next_p=head;
struct app *tmp_p; //保存上一個節(jié)點(diǎn)的地址
//1.申請空間并給空間成員賦值
new_p=malloc(sizeof(struct app));
new_p->a=a;
new_p->next=NULL;
?
//2. 找到鏈表尾
while(next_p!=NULL)
{
tmp_p=next_p;
next_p=next_p->next; //指針指向下一個節(jié)點(diǎn)
}
?
//3. 插入新節(jié)點(diǎn)--鏈接結(jié)尾
tmp_p->next=new_p;
}
?
/*
函數(shù)功能: 遍歷輸出鏈接里的所有數(shù)據(jù)
*/
void list_print(struct app *head)
{
struct app *next_p=head;
int cnt=0;
if(head!=NULL)
{
while(next_p->next!=NULL)
{
next_p=next_p->next;
printf("鏈表節(jié)點(diǎn)[%d]:a=%d\n",cnt++,next_p->a);
}
}
}
?
/*
函數(shù)功能:鏈表的刪除--按照指定的數(shù)據(jù)刪除
*/
void list_del(int a,struct app *head)
{
struct app *next_p=head;
struct app *tmp_p; //保存上一個節(jié)點(diǎn)的地址
//1. 找到要刪除的鏈表
if(next_p!=NULL)
{
while(next_p->next!=NULL)
{
tmp_p=next_p; //保存上一個節(jié)點(diǎn)的地址
next_p=next_p->next; //獲取有效節(jié)點(diǎn)的地址
if(next_p->a==a) //判斷是否需要刪除
{
tmp_p->next=next_p->next;
free(next_p);
}
}
}
}
復(fù)制代碼
3. 案例: 單向循環(huán)鏈表
代碼直接在上面的案例2例子上改造的,區(qū)別就是尾結(jié)點(diǎn)指向了頭結(jié)點(diǎn)而不是NULL。
#include
#include
?
//定義鏈表節(jié)點(diǎn)的結(jié)構(gòu)體
struct app
{
int a;
struct app *next; //能保存結(jié)構(gòu)體的地址
};
?
struct app *list_head=NULL; //鏈表的頭指針
?
void list_print(struct app *head);
struct app *list_HeadInit(struct app *head);
void list_add(int a,struct app *head);
void list_del(int a,struct app *head);
?
int main()
{
//1. 初始化鏈表頭
list_head=list_HeadInit(list_head);
//2. 在鏈表尾插入數(shù)據(jù)
list_add(10,list_head);
list_add(11,list_head);
list_add(12,list_head);
list_add(13,list_head);
//3. 刪除節(jié)點(diǎn)
list_del(11,list_head);
//4. 輸出鏈接節(jié)點(diǎn)里的數(shù)據(jù)
list_print(list_head);
return 0;
}
?
/*
函數(shù)功能: 初始化鏈表頭--給鏈表頭申請空間
*/
struct app *list_HeadInit(struct app *head)
{
if(head==NULL) //沒有空間
{
//1. 申請鏈表頭空間
head=malloc(sizeof(struct app));
//2. 初始化鏈表頭
head->next=head;
}
return head;
}
?
/*
函數(shù)功能: 在鏈表尾插入數(shù)據(jù)
int a 插入的數(shù)據(jù)值
struct app *head 鏈表頭
*/
void list_add(int a,struct app *head)
{
struct app *new_p=NULL;
struct app *next_p=head;
struct app *tmp_p; //保存上一個節(jié)點(diǎn)的地址
//1.申請空間并給空間成員賦值
new_p=malloc(sizeof(struct app));
new_p->a=a;
new_p->next=head;
?
//2. 找到鏈表尾
if(head!=NULL)
{
if(next_p->next==head) //表示第一次插入節(jié)點(diǎn)
{
next_p->next=new_p;
//head ----<節(jié)點(diǎn)1>---head
}
else
{
while(next_p->next!=head)
{
next_p=next_p->next; //指針指向下一個節(jié)點(diǎn)
}
//3. 插入新節(jié)點(diǎn)--鏈接結(jié)尾
next_p->next=new_p;
}
}
}
?
/*
函數(shù)功能: 遍歷輸出鏈接里的所有數(shù)據(jù)
*/
void list_print(struct app *head)
{
struct app *next_p=head;
int cnt=0;
if(head!=NULL)
{
printf("頭地址: %#x\n",next_p); //頭
printf("第一個節(jié)點(diǎn)地址:%#x\n",next_p->next); //下一個節(jié)點(diǎn)地址
printf("第二個節(jié)點(diǎn)地址:%#x\n",next_p->next->next); //下下一個節(jié)點(diǎn)地址
printf("第三個節(jié)點(diǎn)地址:%#x\n",next_p->next->next->next);
printf("第四個節(jié)點(diǎn)地址:%#x\n",next_p->next->next->next->next);
while(next_p->next!=head)
{
next_p=next_p->next;
printf("鏈表節(jié)點(diǎn)[%d]:a=%d\n",cnt++,next_p->a);
}
}
}
?
/*
函數(shù)功能:鏈表的刪除--按照指定的數(shù)據(jù)刪除
*/
void list_del(int a,struct app *head)
{
struct app *next_p=head;
struct app *tmp_p; //保存上一個節(jié)點(diǎn)的地址
//1. 找到要刪除的鏈表
if(next_p!=NULL)
{
while(next_p->next!=head)
{
tmp_p=next_p; //保存上一個節(jié)點(diǎn)的地址
next_p=next_p->next; //獲取有效節(jié)點(diǎn)的地址
if(next_p->a==a) //判斷是否需要刪除
{
tmp_p->next=next_p->next;
free(next_p);
}
}
}
}
復(fù)制代碼
4. 案例: 創(chuàng)建雙向鏈表循環(huán),實現(xiàn)插入、刪除、遍歷
雙向鏈表在每個節(jié)點(diǎn)里新增加了一個指針,用于保存上一個節(jié)點(diǎn)的地址,現(xiàn)在的節(jié)點(diǎn)里一個用兩個指針,一個保存上一個節(jié)點(diǎn)的地址,一個保存下一個節(jié)點(diǎn)的地址。
#include
#include
?
//定義鏈表節(jié)點(diǎn)的結(jié)構(gòu)體
struct app
{
int a;
struct app *next; //下一個節(jié)點(diǎn)地址
struct app *prev; //前一個節(jié)點(diǎn)地址
};
?
//全局變量聲明區(qū)域
struct app *list_head=NULL; //鏈表的頭指針
?
//函數(shù)聲明
struct app *List_HeadInit(struct app *head);
void list_add(int a,struct app *head);
void list_print(struct app *head);
void list_del(int a,struct app *head);
?
int main()
{
/*1. 初始化鏈表*/
list_head=List_HeadInit(list_head);
/*2. 添加鏈表節(jié)點(diǎn)*/
list_add(10,list_head);
list_add(11,list_head);
list_add(12,list_head);
list_add(13,list_head);
list_add(14,list_head);
/*3.刪除指定節(jié)點(diǎn)*/
list_del(12,list_head);
/*4. 遍歷輸出所有節(jié)點(diǎn)信息*/
list_print(list_head);
return 0;
}
?
/*
函數(shù)功能: 創(chuàng)建鏈表頭
*/
struct app *List_HeadInit(struct app *head)
{
if(head==NULL)
{
head=malloc(sizeof(struct app));
head->a=0;
head->next=head;
head->prev=head;
}
return head;
}
?
/*
函數(shù)功能: 添加數(shù)據(jù)-鏈表尾添加數(shù)據(jù)
*/
void list_add(int a,struct app *head)
{
struct app *next_p=head;
struct app *new_p=NULL;
/*1. 申請新的節(jié)點(diǎn)*/
new_p=malloc(sizeof(struct app));
new_p->a=a;
new_p->next=head;
/*2. 完成新節(jié)點(diǎn)的添加*/
//遍歷鏈表
while(next_p->next!=head)
{
next_p=next_p->next;
}
//添加新節(jié)點(diǎn)
new_p->prev=next_p;
next_p->next=new_p;
//修改鏈表頭的上一個節(jié)點(diǎn)地址
head->prev=new_p;
}
?
/*
函數(shù)功能:輸出鏈表里的所有數(shù)據(jù)
*/
void list_print(struct app *head)
{
struct app *next_p=head;
int cnt=0;
/*1. 順向遍歷*/
while(next_p->next!=head)
{
next_p=next_p->next;
printf("節(jié)點(diǎn)[%d]:%d\n",cnt++,next_p->a);
}
/*2. 反向遍歷*/
next_p=head;
while(next_p->prev!=head)
{
next_p=next_p->prev;
printf("節(jié)點(diǎn)[%d]:%d\n",cnt--,next_p->a);
}
}
?
/*
函數(shù)功能:刪除鏈表里的指定節(jié)點(diǎn)
*/
void list_del(int a,struct app *head)
{
struct app *next_p=head;
struct app *tmp_p=NULL;
while(next_p->next!=head)
{
tmp_p=next_p; //保存上一個節(jié)點(diǎn)的地址
next_p=next_p->next;
if(next_p->a==a)
{
//方式1
tmp_p->next=tmp_p->next->next;
tmp_p->next->prev=tmp_p;
?
//方式2
//tmp_p->next=next_p->next;
//next_p->next->prev=tmp_p;
//printf("%d\n",tmp_p->a); //11
//printf("%d\n",tmp_p->next->a); //13
//printf("%d\n",next_p->next->prev->a); //11
free(next_p);
break;
}
}
}
審核編輯 黃昊宇
-
嵌入式
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
5147文章
19627瀏覽量
316675 -
C語言
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
180文章
7631瀏覽量
141217
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
C語言實現(xiàn)動態(tài)鏈表的建立
C語言算法題:反轉(zhuǎn)一個單向鏈表
C語言單向鏈表
C語言玩轉(zhuǎn)鏈表
玩轉(zhuǎn)C語言鏈表-鏈表各類操作詳解
C語言實現(xiàn)單鏈表舉例
了解Linux通用的雙向循環(huán)鏈表
雙向循環(huán)鏈表的創(chuàng)建
C語言_鏈表總結(jié)
單鏈表和雙鏈表的區(qū)別在哪里
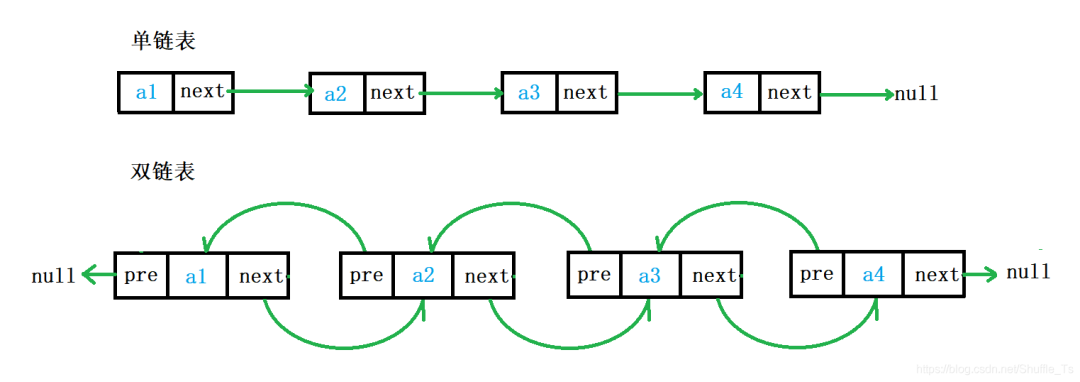





 C語言-鏈表(單向鏈表、雙向鏈表)
C語言-鏈表(單向鏈表、雙向鏈表)











評論