前言
搜索是大數據領域里常見的需求。Splunk和ELK分別是該領域在非開源和開源領域里的領導者。本文利用很少的Python代碼實現了一個基本的數據搜索功能,試圖讓大家理解大數據搜索的基本原理。
布隆過濾器 (Bloom Filter)
第一步我們先要實現一個布隆過濾器。
布隆過濾器是大數據領域的一個常見算法,它的目的是過濾掉那些不是目標的元素。也就是說如果一個要搜索的詞并不存在與我的數據中,那么它可以以很快的速度返回目標不存在。
讓我們看看以下布隆過濾器的代碼:
classBloomfilter(object):
A Bloom filter is a probabilistic data-structure that trades space for accuracy
when determining if a value is in a set.It can tell you if a value was possibly
added, or if it was definitely not added, but it can't tell you for certain that
it was added.
"""
def __init__(self,size):
"""Setup the BF with the appropriate size"""
self.values = [False] * size
self.size = size
def hash_value(self,value):
"""Hash the value provided and scale it to fit the BF size"""
returnhash(value) % self.size
def add_value(self,value):
"""Add a value to the BF"""
h = self.hash_value(value)
self.values[h] = True
def might_contain(self,value):
"""Check if the value might be in the BF"""
h = self.hash_value(value)
returnself.values[h]
def print_contents(self):
"""Dump the contents of the BF for debugging purposes"""
print self.values
基本的數據結構是個數組(實際上是個位圖,用1/0來記錄數據是否存在),初始化是沒有任何內容,所以全部置False。實際的使用當中,該數組的長度是非常大的,以保證效率。
利用哈希算法來決定數據應該存在哪一位,也就是數組的索引
當一個數據被加入到布隆過濾器的時候,計算它的哈希值然后把相應的位置為True
當檢查一個數據是否已經存在或者說被索引過的時候,只要檢查對應的哈希值所在的位的True/Fasle
看到這里,大家應該可以看出,如果布隆過濾器返回False,那么數據一定是沒有索引過的,然而如果返回True,那也不能說數據一定就已經被索引過。在搜索過程中使用布隆過濾器可以使得很多沒有命中的搜索提前返回來提高效率。
我們看看這段 code是如何運行的:
bf = Bloomfilter(10)
bf.add_value('dog')
bf.add_value('fish')
bf.add_value('cat')
bf.print_contents()
bf.add_value('bird')
bf.print_contents()
# Note: contents are unchanged after adding bird - it collides
forterm in['dog','fish','cat','bird','duck','emu']:
print'{}: {} {}'.format(term,bf.hash_value(term),bf.might_contain(term))
結果:
[False,False,False,False,True,True,False,False,False,True]
[False,False,False,False,True,True,False,False,False,True]
dog: 5True
fish: 4True
cat: 9True
bird: 9True
duck: 5True
emu: 8False
首先創建了一個容量為10的的布隆過濾器
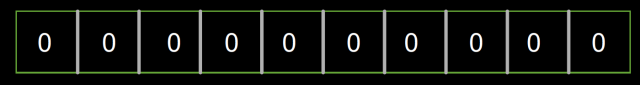
然后分別加入 ‘dog’,‘fish’,‘cat’三個對象,這時的布隆過濾器的內容如下:
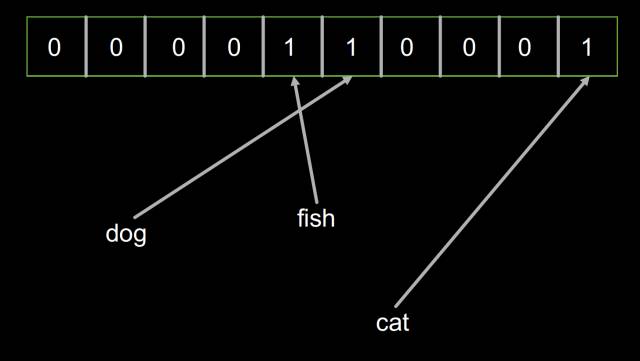
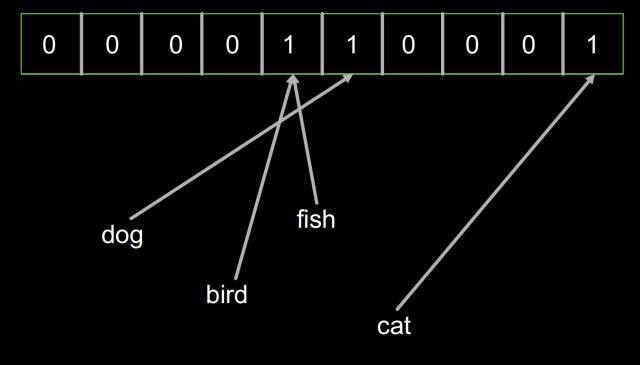
然后加入‘bird’對象,布隆過濾器的內容并沒有改變,因為‘bird’和‘fish’恰好擁有相同的哈希。
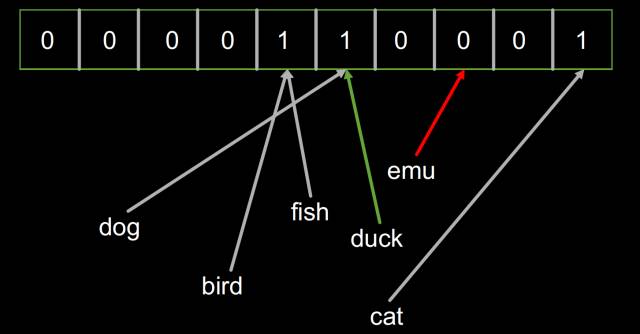
最后我們檢查一堆對象(’dog’, ‘fish’, ‘cat’, ‘bird’, ‘duck’, ’emu’)是不是已經被索引了。結果發現‘duck’返回True,2而‘emu’返回False。因為‘duck’的哈希恰好和‘dog’是一樣的。
分詞
下面一步我們要實現分詞。 分詞的目的是要把我們的文本數據分割成可搜索的最小單元,也就是詞。這里我們主要針對英語,因為中文的分詞涉及到自然語言處理,比較復雜,而英文基本只要用標點符號就好了。
下面我們看看分詞的代碼:
def major_segments(s):
"""
Perform major segmenting on a string.Split the string by all of the major
breaks, and return the set of everything found.The breaks in this implementation
are single characters, but in Splunk proper they can be multiple characters.
A set is used because ordering doesn't matter, and duplicates are bad.
"""
major_breaks = ' '
last = -1
results = set()
# enumerate() will give us (0, s[0]), (1, s[1]), ...
foridx,ch inenumerate(s):
ifch inmajor_breaks:
segment = s[last+1:idx]
results.add(segment)
last = idx
# The last character may not be a break so always capture
# the last segment (which may end up being "", but yolo)
segment = s[last+1:]
results.add(segment)
returnresults
主要分割
主要分割使用空格來分詞,實際的分詞邏輯中,還會有其它的分隔符。例如Splunk的缺省分割符包括以下這些,用戶也可以定義自己的分割符。
] < >( ) { } | ! ; , ‘ ” * s & ? + %21 %26 %2526 %3B %7C %20 %2B %3D — %2520 %5D %5B %3A %0A %2C %28 %29
def minor_segments(s):
"""
Perform minor segmenting on a string.This is like major
segmenting, except it also captures from the start of the
input to each break.
"""
minor_breaks = '_.'
last = -1
results = set()
foridx,ch inenumerate(s):
ifch inminor_breaks:
segment = s[last+1:idx]
results.add(segment)
segment = s[:idx]
results.add(segment)
last = idx
segment = s[last+1:]
results.add(segment)
results.add(s)
returnresults
次要分割
次要分割和主要分割的邏輯類似,只是還會把從開始部分到當前分割的結果加入。例如“1.2.3.4”的次要分割會有1,2,3,4,1.2,1.2.3
def segments(event):
"""Simple wrapper around major_segments / minor_segments"""
results = set()
formajor inmajor_segments(event):
forminor inminor_segments(major):
results.add(minor)
returnresults
分詞的邏輯就是對文本先進行主要分割,對每一個主要分割在進行次要分割。然后把所有分出來的詞返回。
我們看看這段 code是如何運行的:
forterm insegments('src_ip = 1.2.3.4'):
print term
src
1.2
1.2.3.4
src_ip
3
1
1.2.3
ip
2
=
4
搜索
好了,有個分詞和布隆過濾器這兩個利器的支撐后,我們就可以來實現搜索的功能了。
上代碼:
classSplunk(object):
def __init__(self):
self.bf = Bloomfilter(64)
self.terms = {}# Dictionary of term to set of events
self.events = []
def add_event(self,event):
"""Adds an event to this object"""
# Generate a unique ID for the event, and save it
event_id = len(self.events)
self.events.append(event)
# Add each term to the bloomfilter, and track the event by each term
forterm insegments(event):
self.bf.add_value(term)
ifterm notinself.terms:
self.terms[term] = set()
self.terms[term].add(event_id)
def search(self,term):
"""Search for a single term, and yield all the events that contain it"""
# In Splunk this runs in O(1), and is likely to be in filesystem cache (memory)
ifnotself.bf.might_contain(term):
return
# In Splunk this probably runs in O(log N) where N is the number of terms in the tsidx
ifterm notinself.terms:
return
forevent_id insorted(self.terms[term]):
yield self.events[event_id]
Splunk代表一個擁有搜索功能的索引集合
每一個集合中包含一個布隆過濾器,一個倒排詞表(字典),和一個存儲所有事件的數組
當一個事件被加入到索引的時候,會做以下的邏輯
為每一個事件生成一個unqie id,這里就是序號
對事件進行分詞,把每一個詞加入到倒排詞表,也就是每一個詞對應的事件的id的映射結構,注意,一個詞可能對應多個事件,所以倒排表的的值是一個Set。倒排表是絕大部分搜索引擎的核心功能。
當一個詞被搜索的時候,會做以下的邏輯
檢查布隆過濾器,如果為假,直接返回
檢查詞表,如果被搜索單詞不在詞表中,直接返回
在倒排表中找到所有對應的事件id,然后返回事件的內容
我們運行下看看把:
s = Splunk()
s.add_event('src_ip = 1.2.3.4')
s.add_event('src_ip = 5.6.7.8')
s.add_event('dst_ip = 1.2.3.4')
forevent ins.search('1.2.3.4'):
print event
print'-'
forevent ins.search('src_ip'):
print event
print'-'
forevent ins.search('ip'):
print event
src_ip = 1.2.3.4
dst_ip = 1.2.3.4
-
src_ip = 1.2.3.4
src_ip = 5.6.7.8
-
src_ip = 1.2.3.4
src_ip = 5.6.7.8
dst_ip = 1.2.3.4
是不是很贊!
更復雜的搜索
更進一步,在搜索過程中,我們想用And和Or來實現更復雜的搜索邏輯。
上代碼:
classSplunkM(object):
def __init__(self):
self.bf = Bloomfilter(64)
self.terms = {}# Dictionary of term to set of events
self.events = []
def add_event(self,event):
"""Adds an event to this object"""
# Generate a unique ID for the event, and save it
event_id = len(self.events)
self.events.append(event)
# Add each term to the bloomfilter, and track the event by each term
forterm insegments(event):
self.bf.add_value(term)
ifterm notinself.terms:
self.terms[term] = set()
self.terms[term].add(event_id)
def search_all(self,terms):
"""Search for an AND of all terms"""
# Start with the universe of all events...
results = set(range(len(self.events)))
forterm interms:
# If a term isn't present at all then we can stop looking
ifnotself.bf.might_contain(term):
return
ifterm notinself.terms:
return
# Drop events that don't match from our results
results = results.intersection(self.terms[term])
forevent_id insorted(results):
yield self.events[event_id]
def search_any(self,terms):
"""Search for an OR of all terms"""
results = set()
forterm interms:
# If a term isn't present, we skip it, but don't stop
ifnotself.bf.might_contain(term):
continue
ifterm notinself.terms:
continue
# Add these events to our results
results = results.union(self.terms[term])
forevent_id insorted(results):
yield self.events[event_id]
利用Python集合的intersection和union操作,可以很方便的支持And(求交集)和Or(求合集)的操作。
運行結果如下:
s = SplunkM()
s.add_event('src_ip = 1.2.3.4')
s.add_event('src_ip = 5.6.7.8')
s.add_event('dst_ip = 1.2.3.4')
forevent ins.search_all(['src_ip','5.6']):
print event
print'-'
forevent ins.search_any(['src_ip','dst_ip']):
print event
src_ip = 5.6.7.8
-
src_ip = 1.2.3.4
src_ip = 5.6.7.8
dst_ip = 1.2.3.4
總結
以上的代碼只是為了說明大數據搜索的基本原理,包括布隆過濾器,分詞和倒排表。如果大家真的想要利用這代碼來實現真正的搜索功能,還差的太遠。所有的內容來自于Splunk Conf2017。大家如果有興趣可以去看網上的視頻。
-
python
+關注
關注
56文章
4827瀏覽量
86656
原文標題:用 Python 實現一個大數據搜索引擎
文章出處:【微信號:magedu-Linux,微信公眾號:馬哥Linux運維】歡迎添加關注!文章轉載請注明出處。
發布評論請先 登錄
OpenAI免費開放ChatGPT搜索功能
LZO Data Compression,高性能LZO無損數據壓縮加速器介紹,FPGA&ASIC
javascript:void(0) 是否影響SEO優化
蘋果為谷歌支付數十億美元辯護,參與搜索案反壟斷審判
SSR的優勢和劣勢分析
阿里國際推出全球首個B2B AI搜索引擎Accio
阿里國際推出B2B領域AI搜索引擎Accio
租用多ip云服務器可以帶來哪些好處?應用場景有哪些?
OpenAI推出ChatGPT搜索功能
Meta開發新搜索引擎,減少對谷歌和必應的依賴
月訪問量超2億,增速113%!360AI搜索成為全球增速最快的AI搜索引擎





 用 Python 實現一個大數據搜索引擎
用 Python 實現一個大數據搜索引擎











評論