有時(shí),由于波動(dòng),人們發(fā)現(xiàn)很難從模擬溫度計(jì)讀取溫度。因此,在這里我們將使用8051微控制器構(gòu)建一個(gè)簡(jiǎn)單的數(shù)字溫度計(jì),其中LM35傳感器用于測(cè)量溫度。我們還使用LM35構(gòu)建使用Arduino,NodeMCU,PIC,Raspberry Pi和其他微控制器的數(shù)字溫度計(jì)。
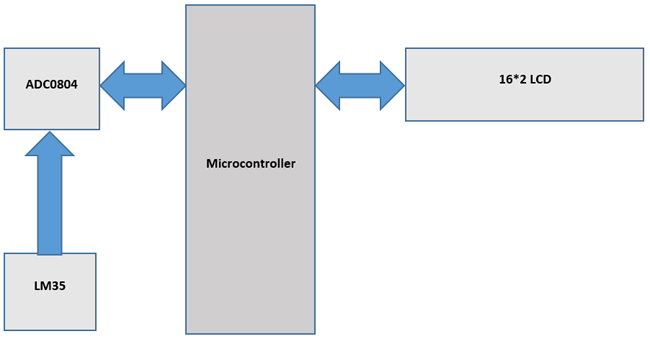
該項(xiàng)目還將作為ADC0804與8051和16*2 LCD與8051微控制器的適當(dāng)接口。
所需組件:
8051開發(fā)板
ADC0804 板
16*2液晶顯示屏
LM35 傳感器
電位計(jì)
跳線
電路圖:
使用LM35的數(shù)字溫度計(jì)電路的電路圖如下:

使用 35 使用 8051 測(cè)量溫度:
8051微控制器是一個(gè)8位微控制器,具有128字節(jié)的片上RAM,4K字節(jié)的片上ROM,兩個(gè)定時(shí)器,一個(gè)串行端口和四個(gè)8位端口。8052微控制器是微控制器的擴(kuò)展。下表顯示了8051名家庭成員的比較。
| 特征 | 8051 | 8052 |
| 只讀存儲(chǔ)器(以字節(jié)為單位) | 4K | 8K |
| 內(nèi)存(字節(jié)) | 128 | 256 |
| 定時(shí)器 | 2 | 3 |
| I/O 引腳 | 32 | 32 |
| 串行端口 | 1 | 1 |
| 中斷源 | 6 | 8 |
16x2 液晶顯示器:
16 * 2 LCD是嵌入式應(yīng)用中廣泛使用的顯示器。以下是有關(guān)16 * 2液晶顯示器的引腳和工作的簡(jiǎn)要說明。LCD內(nèi)部有兩個(gè)非常重要的寄存器。它們是數(shù)據(jù)寄存器和命令寄存器。命令寄存器用于發(fā)送清晰顯示、光標(biāo)在家鄉(xiāng)等命令,數(shù)據(jù)寄存器用于發(fā)送要在16*2 LCD上顯示的數(shù)據(jù)。下表顯示了16 * 2 LCD的引腳說明。
| 針 | 象征 | I/O | 描述 |
| 1 | VSS | - | 地 |
| 2 | Vdd | - | +5V電源 |
| 3 | V形 | - | 用于控制對(duì)比度的電源 |
| 4 | RS | 我 |
RS=0 為命令寄存器 , RS=1 用于數(shù)據(jù)寄存器 |
| 5 | 烏爾曼 | 我 | R/W=0 表示寫入,R/W=1 表示讀取 |
| 6 | E | I/O | 使 |
| 7 | D0 | I/O | 8位數(shù)據(jù)總線 |
| 8 | D1 | I/O | 8位數(shù)據(jù)總線 |
| 9 | D2 | I/O | 8位數(shù)據(jù)總線 |
| 10 | D3 | I/O | 8位數(shù)據(jù)總線 |
| 11 | D4 | I/O | 8位數(shù)據(jù)總線 |
| 12 | D5 | I/O | 8位數(shù)據(jù)總線 |
| 13 | D6 | I/O | 8位數(shù)據(jù)總線 |
| 14 | D7 | I/O | 8位數(shù)據(jù)總線 |
| 15 | 一個(gè) | - | +5V背光 |
| 16 | K | - | 地 |
下表顯示了常用的液晶屏命令代碼。
| 代碼(十六進(jìn)制) | 描述 |
| 01 | 清晰的顯示屏 |
| 06 | 遞增光標(biāo)(右移) |
| 0安 | 顯示關(guān)閉,光標(biāo)打開 |
| 0C | 顯示打開,光標(biāo)關(guān)閉 |
| 0F | 顯示于 ,光標(biāo)閃爍 |
| 80 | 強(qiáng)制光標(biāo)從 1 開始圣線 |
| C0 | 強(qiáng)制光標(biāo)以 2 開頭德·線 |
| 38 | 2行和5 * 7矩陣 |
ADC0804 集成電路:
ADC0804 IC是美國(guó)國(guó)家半導(dǎo)體公司ADC0800系列中的8位并行ADC。它的工作電壓為+5伏,分辨率為8位。步長(zhǎng)和 VIN 范圍因 Vref/2 的不同值而異。下表顯示了 Vref/2 和 VIN 范圍之間的關(guān)系。
| Vref/2 (V) | 葡萄酒 (V) | 步長(zhǎng)(mV) |
| 打開 | 0 到 5 | 19.53 |
| 2.0 | 0 到 4 | 15.62 |
| 1.5 | 0 到 3 | 11.71 |
| 1.28 | 0 到 2.56 | 10 |
在我們的例子中,Vref/2連接到1.28伏,因此步長(zhǎng)為10mV。對(duì)于ADC0804,步長(zhǎng)計(jì)算為(2 * Vref / 2)/256。
以下公式用于計(jì)算輸出電壓:
Dout = Vin / step size
其中Dout是以十進(jìn)制輸出的數(shù)字?jǐn)?shù)據(jù),Vin =模擬輸入電壓和步長(zhǎng)(分辨率)是最小的變化。在此處了解有關(guān)ADC0804的更多信息,還可以檢查ADC0808與8051的接口。
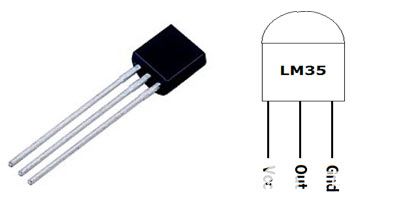
LM35 溫度傳感器:
LM35 是一款溫度傳感器,其輸出電壓與攝氏溫度成線性比例。LM35 已經(jīng)校準(zhǔn),因此不需要外部校準(zhǔn)。它每攝氏度溫度輸出 10mV。
LM35 傳感器產(chǎn)生與溫度相對(duì)應(yīng)的電壓。該電壓由ADC0804轉(zhuǎn)換為數(shù)字(0至256),并饋送到8051微控制器。8051微控制器將此數(shù)字值轉(zhuǎn)換為以攝氏度為單位的溫度。然后將該溫度轉(zhuǎn)換為適合顯示的ascii形式。此 ascii 值被饋送到 16*2 LCD,該 LCD 在其屏幕上顯示溫度。此過程在指定的時(shí)間間隔后重復(fù)。
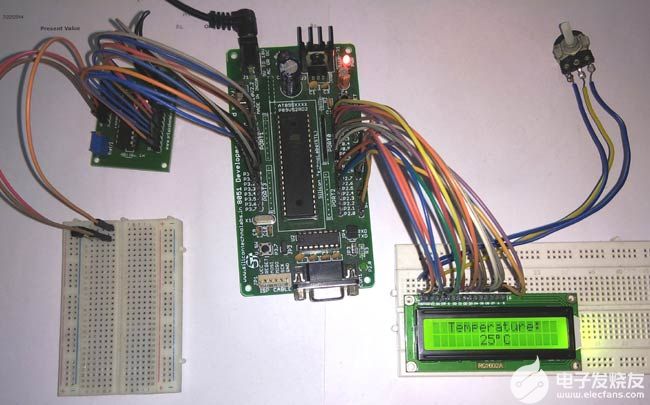
以下是使用 8051 的 LM35 數(shù)字溫度計(jì)的設(shè)置映像:
您可以在此處找到所有基于 LM35 的數(shù)字溫度計(jì)。
代碼說明:
使用LM35的數(shù)字溫度計(jì)的完整C程序在本項(xiàng)目結(jié)束時(shí)給出。代碼被分成有意義的小塊,并在下面解釋。
對(duì)于 16*2 LCD 與 8051 微控制器接口 ,我們必須定義 16*2 LCD 連接到 8051 微控制器的引腳。16*2 LCD 的 RS 引腳連接到 P2.7,16*2 LCD 的 RW 引腳連接到 P2.6,16*2 LCD 的 E 引腳連接到 P2.5。數(shù)據(jù)引腳連接到 8051 微控制器的端口 0。
sbit rs=P2^7; //Register Select(RS) pin of 16*2 lcd
sbit rw=P2^6; //Read/Write(RW) pin of 16*2 lcd
sbit en=P2^5; //Enable(E) pin of 16*2 lcd
同樣,對(duì)于ADC0804與8051微控制器的接口,我們必須定義ADC0804連接到8051微控制器的引腳。ADC0804的RD引腳連接到P3.0,ADC0804的WR引腳連接到P3.1,ADC0804的INTR引腳連接到P3.2。數(shù)據(jù)引腳連接到 8051 微控制器的端口 1。
sbit rd_adc=P3^0; //Read(RD) pin of ADC0804
sbit wr_adc=P3^1; //Write(WR) pin of ADC0804
sbit intr_adc=P3^2; //Interrupt(INTR) pin of ADC0804
接下來,我們必須定義一些在程序中使用的函數(shù)。延時(shí)功能用于創(chuàng)建指定的時(shí)間延遲,c mdwrt功能用于向16 * 2 LCD顯示器發(fā)送命令,datawrt功能用于將數(shù)據(jù)發(fā)送到16 * 2 LCD顯示器,convert_display功能用于將ADC數(shù)據(jù)轉(zhuǎn)換為溫度并將其顯示在16 * 2 LCD顯示器上。
void delay(unsigned int) ; //function for creating delay
void cmdwrt(unsigned char); //function for sending commands to 16*2 lcd display
void datawrt(unsigned char); //function for sending data to 16*2 lcd display
void convert_display(unsigned char); //function for converting ADC value to temperature and display it on 16*2 lcd display
在下面的代碼部分中,我們將命令發(fā)送到 16*2 lcd。清除顯示、遞增光標(biāo)、強(qiáng)制光標(biāo)以 1 開頭等命令圣在指定的時(shí)間延遲后,線被一一發(fā)送到16 * 2液晶顯示器。
for(i=0;i<5;i++) //send commands to 16*2 lcd display one command at a time
{
cmdwrt(cmd[i]); //function call to send commands to 16*2 lcd display
delay(1);
}
在代碼的這一部分中,我們將數(shù)據(jù)發(fā)送到 16*2 lcd。要在16 * 2 LCD顯示屏上顯示的數(shù)據(jù)在指定的時(shí)間延遲后被逐個(gè)發(fā)送以顯示。
for(i=0;i<12;i++) //send data to 16*2 lcd display one character at a time
{
datawrt(data1[i]); //function call to send data to 16*2 lcd display
delay(1);
}
在代碼的這一部分中,我們將LM35傳感器產(chǎn)生的模擬電壓轉(zhuǎn)換為數(shù)字?jǐn)?shù)據(jù),然后將其轉(zhuǎn)換為溫度并顯示在16 * 2 LCD顯示屏上。為了使ADC0804開始轉(zhuǎn)換,我們必須在ADC0804的WR引腳上發(fā)送低到高脈沖,然后我們必須等待轉(zhuǎn)換結(jié)束。INTR 在轉(zhuǎn)換結(jié)束時(shí)變低。一旦INTR變?yōu)榈碗娖剑琑D就會(huì)變?yōu)榈碗娖剑詫?shù)字?jǐn)?shù)據(jù)復(fù)制到8051微控制器的端口0。在指定的時(shí)間延遲后,下一個(gè)周期開始。這個(gè)過程將永遠(yuǎn)重復(fù)。
while(1) //repeat forever
{
wr_adc=0; //send LOW to HIGH pulse on WR pin
delay(1);
wr_adc=1;
while(intr_adc==1); //wait for End of Conversion
rd_adc=0; //make RD = 0 to read the data from ADC0804
value=P1; //copy ADC data
convert_display(value); //function call to convert ADC data into temperature and display it on 16*2 lcd display
delay(1000); //interval between every cycles
rd_adc=1; //make RD = 1 for the next cycle
}
在下面的部分代碼中,我們將命令發(fā)送到 16*2 LCD 顯示器。該命令將復(fù)制到 8051 微控制器的端口 0。對(duì)于命令寫入,RS 設(shè)置為低電平。對(duì)于寫入操作,RW 設(shè)置為低電平。在使能(E)引腳上施加高到低脈沖以啟動(dòng)命令寫入操作。
void cmdwrt (unsigned char x)
{
P0=x; //send the command to Port 0 on which 16*2 lcd is connected
rs=0; //make RS = 0 for command
rw=0; //make RW = 0 for write operation
en=1; //send a HIGH to LOW pulse on Enable(E) pin to start commandwrite operation
delay(1);
en=0;
}
在代碼的這一部分中,我們將數(shù)據(jù)發(fā)送到16 * 2 LCD顯示器。數(shù)據(jù)將復(fù)制到 8051 微控制器的端口 0。RS 設(shè)置為高,用于命令寫入。對(duì)于寫入操作,RW 設(shè)置為低電平。在使能(E)引腳上施加高到低脈沖以啟動(dòng)數(shù)據(jù)寫入操作。
void datawrt (unsigned char y)
{
P0=y; //send the data to Port 0 on which 16*2 lcd is connected
rs=1; //make RS = 1 for command
rw=0; //make RW = 0 for write operation
en=1; //send a HIGH to LOW pulse on Enable(E) pin to start datawrite operation
delay(1);
en=0;
}
在代碼的這一部分中,我們將數(shù)字?jǐn)?shù)據(jù)轉(zhuǎn)換為溫度并將其顯示在16 * 2 LCD顯示屏上。
void convert_display(unsigned char value)
{
unsigned char x1,x2,x3;
cmdwrt(0xc6); //command to set the cursor to 6th position of 2nd line on 16*2 lcd
x1=(value/10); //divide the value by 10 and store quotient in variable x1
x1=x1+(0x30); //convert variable x1 to ascii by adding 0x30
x2=value%10; //divide the value by 10 and store remainder in variable x2
x2=x2+(0x30); //convert variable x2 to ascii by adding 0x30
x3=0xDF; //ascii value of degree(°) symbol
datawrt(x1); //display temperature on 16*2 lcd display
datawrt(x2);
datawrt(x3);
datawrt('C');
}
完整代碼:
/*this program is for displaying the temperature on 16*2 lcd display using 8051 microcontroller , LM35 sensor and ADC0804*/
#include
sbit rs=P2^7; //Register Select(RS) pin of 16*2 lcd
sbit rw=P2^6; //Read/Write(RW) pin of 16*2 lcd
sbit en=P2^5; //Enable(E) pin of 16*2 lcd
sbit rd_adc=P3^0; //Read(RD) pin of ADC0804
sbit wr_adc=P3^1; //Write(WR) pin of ADC0804
sbit intr_adc=P3^2; //Interrupt(INTR) pin of ADC0804
void delay(unsigned int) ; //function for creating delay
void cmdwrt(unsigned char); //function for sending commands to 16*2 lcd display
void datawrt(unsigned char); //function for sending data to 16*2 lcd display
void convert_display(unsigned char); //function for converting ADC value to temperature and display it on 16*2 lcd display
void main(void) //main function
{
unsigned char i;
unsigned char cmd[]={0x38,0x01,0x06,0x0c,0x82};//16*2 lcd initialization commands
unsigned char data1[]="Temperature:";
unsigned char value;
P1=0xFF; //make Port 1 as input port
P0=0x00; //make Port 0 as output port
for(i=0;i<5;i++) //send commands to 16*2 lcd display one command at a time
{
cmdwrt(cmd[i]); //function call to send commands to 16*2 lcd display
delay(1);
}
for(i=0;i<12;i++) //send data to 16*2 lcd display one character at a time
{
datawrt(data1[i]); //function call to send data to 16*2 lcd display
delay(1);
}
intr_adc=1; //make INTR pin as input
rd_adc=1; //set RD pin HIGH
wr_adc=1; //set WR pin LOW
while(1) //repeat forever
{
wr_adc=0; //send LOW to HIGH pulse on WR pin
delay(1);
wr_adc=1;
while(intr_adc==1); //wait for End of Conversion
rd_adc=0; //make RD = 0 to read the data from ADC0804
value=P1; //copy ADC data
convert_display(value); //function call to convert ADC data into temperature and display it on 16*2 lcd display
delay(1000); //interval between every cycles
rd_adc=1; //make RD = 1 for the next cycle
}
}
void cmdwrt (unsigned char x)
{
P0=x; //send the command to Port 0 on which 16*2 lcd is connected
rs=0; //make RS = 0 for command
rw=0; //make RW = 0 for write operation
en=1; //send a HIGH to LOW pulse on Enable(E) pin to start commandwrite operation
delay(1);
en=0;
}
void datawrt (unsigned char y)
{
P0=y; //send the data to Port 0 on which 16*2 lcd is connected
rs=1; //make RS = 1 for command
rw=0; //make RW = 0 for write operation
en=1; //send a HIGH to LOW pulse on Enable(E) pin to start datawrite operation
delay(1);
en=0;
}
void convert_display(unsigned char value)
{
unsigned char x1,x2,x3;
cmdwrt(0xc6); //command to set the cursor to 6th position of 2nd line on 16*2 lcd
x1=(value/10); //divide the value by 10 and store quotient in variable x1
x1=x1+(0x30); //convert variable x1 to ascii by adding 0x30
x2=value%10; //divide the value by 10 and store remainder in variable x2
x2=x2+(0x30); //convert variable x2 to ascii by adding 0x30
x3=0xDF; //ascii value of degree(°) symbol
datawrt(x1); //display temperature on 16*2 lcd display
datawrt(x2);
datawrt(x3);
datawrt('C');
}
void delay(unsigned int z)
{
unsigned int p,q;
for(p=0;p
{
for(q=0;q<1375;q++); //repeat for 1375 times
}
}
-
微控制器
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
48文章
7833瀏覽量
153268 -
8051
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
3文章
311瀏覽量
51990 -
數(shù)字溫度計(jì)
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
3文章
109瀏覽量
22024
發(fā)布評(píng)論請(qǐng)先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
如何使用PIC微控制器和LM35溫度傳感器制作數(shù)字溫度計(jì)
如何使用8051微控制器和藍(lán)牙模塊構(gòu)建一個(gè)Android手機(jī)控制的機(jī)器人
數(shù)字溫度計(jì)的設(shè)計(jì)與實(shí)現(xiàn)
基于D的數(shù)字溫度計(jì)的設(shè)計(jì)
一種基于SWC的數(shù)字溫度計(jì)的設(shè)計(jì)
如何制作數(shù)字溫度計(jì)
利用IC構(gòu)建簡(jiǎn)單的溫度計(jì)式電壓指示
一個(gè)元件制作的數(shù)顯溫度計(jì)電路
數(shù)字溫度計(jì)準(zhǔn)不準(zhǔn)
基于微控制器的數(shù)字溫度計(jì)

使用ATTINY 85制作一個(gè)簡(jiǎn)單的溫度計(jì)

如何創(chuàng)建一個(gè)簡(jiǎn)單的溫度計(jì)






 如何使用8051微控制器構(gòu)建一個(gè)簡(jiǎn)單的數(shù)字溫度計(jì)
如何使用8051微控制器構(gòu)建一個(gè)簡(jiǎn)單的數(shù)字溫度計(jì)










評(píng)論