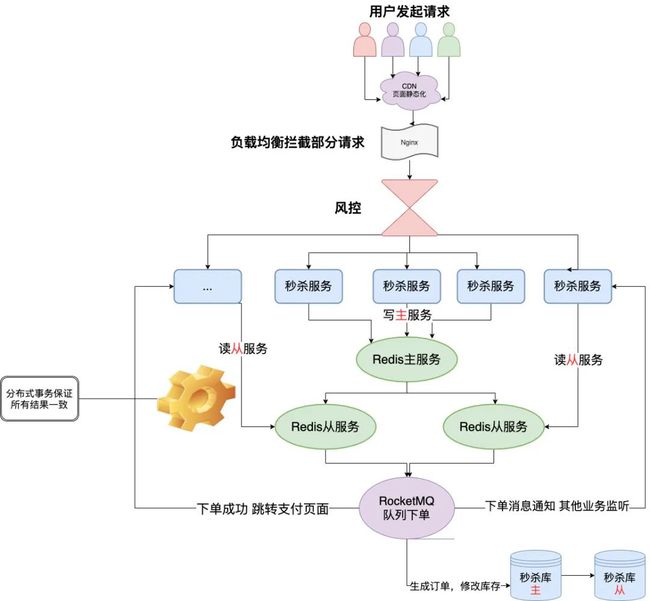
實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)秒殺系統(tǒng),采用spring boot 2.x + mybatis+ redis + swagger2 + lombok實(shí)現(xiàn)。
先說(shuō)說(shuō)基本流程,就是提供一個(gè)秒殺接口,然后針對(duì)秒殺接口進(jìn)行限流,限流的方式目前我實(shí)現(xiàn)了兩種,上次實(shí)現(xiàn)的是累計(jì)計(jì)數(shù)方式,這次還有這個(gè)功能,并且我增加了令牌桶方式的lua腳本進(jìn)行限流。
然后不被限流的數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)來(lái)之后,加一把分布式鎖,獲取分布式鎖之后就可以對(duì)數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)進(jìn)行操作了。直接操作數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)的方式可以,但是速度會(huì)比較慢,咱們直接通過(guò)一個(gè)初始化接口,將庫(kù)存數(shù)據(jù)放到緩存中,然后對(duì)緩存中的數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行操作。
寫(xiě)庫(kù)的操作采用異步方式,實(shí)現(xiàn)的方式就是將操作好的數(shù)據(jù)放入到隊(duì)列中,然后由另一個(gè)線程對(duì)隊(duì)列進(jìn)行消費(fèi)。當(dāng)然,也可以將數(shù)據(jù)直接寫(xiě)入mq中,由另一個(gè)線程進(jìn)行消費(fèi),這樣也更穩(wěn)妥。
好了,看一下項(xiàng)目的基本結(jié)構(gòu):
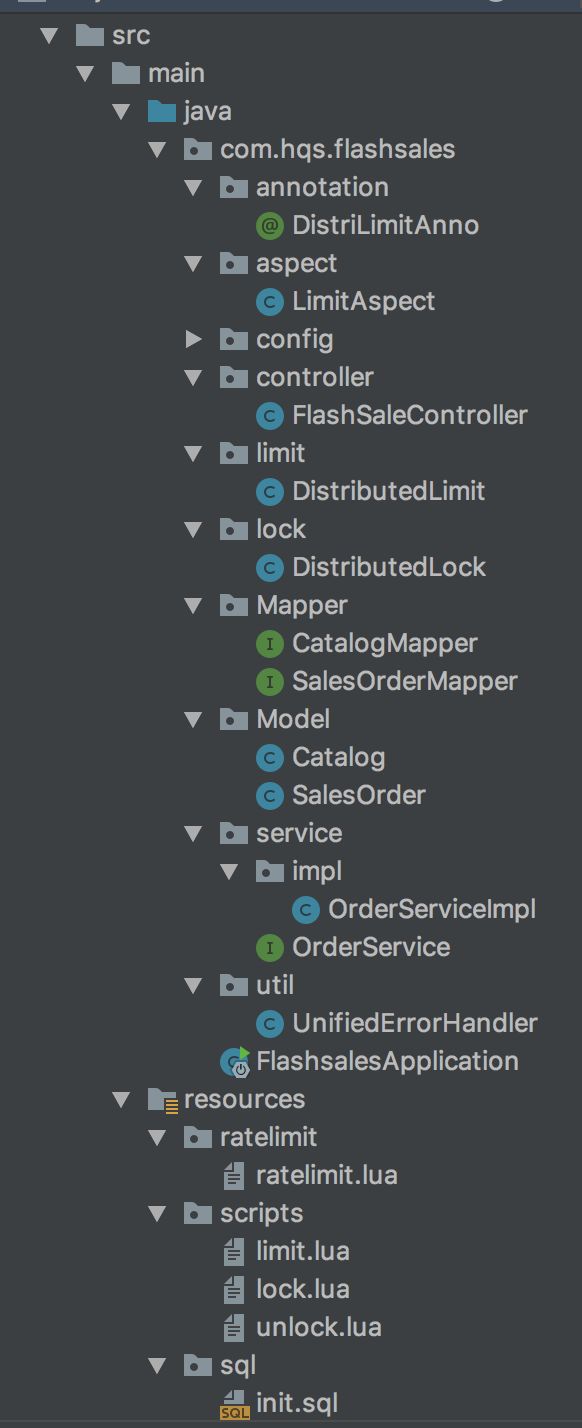
看一下入口controller類(lèi),入口類(lèi)有兩個(gè)方法,一個(gè)是初始化訂單的方法,即秒殺開(kāi)始的時(shí)候,秒殺接口才會(huì)有效,這個(gè)方法可以采用定時(shí)任務(wù)自動(dòng)實(shí)現(xiàn)也可以。
初始化后就可以調(diào)用placeOrder的方法了。在placeOrder上面有個(gè)自定義的注解DistriLimitAnno,這個(gè)是我在上篇文章寫(xiě)的,用作限流使用。
采用的方式目前有兩種,一種是使用計(jì)數(shù)方式限流,一種方式是令牌桶,上次使用了計(jì)數(shù),咱們這次采用令牌桶方式實(shí)現(xiàn)。
package com.hqs.flashsales.controller;
import com.hqs.flashsales.annotation.DistriLimitAnno;import com.hqs.flashsales.aspect.LimitAspect;import com.hqs.flashsales.lock.DistributedLock;import com.hqs.flashsales.limit.DistributedLimit;import com.hqs.flashsales.service.OrderService;import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.RedisScript;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import javax.annotation.Resource;import java.util.Collections;
/** * @author huangqingshi * @Date 2019-01-23 */@Slf4j@Controllerpublic class FlashSaleController {
@Autowired OrderService orderService; @Autowired DistributedLock distributedLock; @Autowired LimitAspect limitAspect; //注意RedisTemplate用的String,String,后續(xù)所有用到的key和value都是String的 @Autowired RedisTemplate
private static final String LOCK_PRE = "LOCK_ORDER";
@PostMapping("/initCatalog") @ResponseBody public String initCatalog() { try { orderService.initCatalog(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("error", e); }
return "init is ok"; }
@PostMapping("/placeOrder") @ResponseBody @DistriLimitAnno(limitKey = "limit", limit = 100, seconds = "1") public Long placeOrder(Long orderId) { Long saleOrderId = 0L; boolean locked = false; String key = LOCK_PRE + orderId; String uuid = String.valueOf(orderId); try { locked = distributedLock.distributedLock(key, uuid, "10" ); if(locked) { //直接操作數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)// saleOrderId = orderService.placeOrder(orderId); //操作緩存 異步操作數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù) saleOrderId = orderService.placeOrderWithQueue(orderId); } log.info("saleOrderId:{}", saleOrderId); } catch (Exception e) { log.error(e.getMessage()); } finally { if(locked) { distributedLock.distributedUnlock(key, uuid); } } return saleOrderId; }
}
令牌桶的方式比直接計(jì)數(shù)更加平滑,直接計(jì)數(shù)可能會(huì)瞬間達(dá)到最高值,令牌桶則把最高峰給削掉了,令牌桶的基本原理就是有一個(gè)桶裝著令牌,然后又一隊(duì)人排隊(duì)領(lǐng)取令牌,領(lǐng)到令牌的人就可以去做做自己想做的事情了,沒(méi)有領(lǐng)到令牌的人直接就走了(也可以重新排隊(duì))。
發(fā)令牌是按照一定的速度發(fā)放的,所以這樣在多人等令牌的時(shí)候,很多人是拿不到的。當(dāng)桶里邊的令牌在一定時(shí)間內(nèi)領(lǐng)完后,則沒(méi)有令牌可領(lǐng),都直接走了。如果過(guò)了一定的時(shí)間之后可以再次把令牌桶裝滿供排隊(duì)的人領(lǐng)。
基本原理是這樣的,看一下腳本簡(jiǎn)單了解一下,里邊有一個(gè)key和四個(gè)參數(shù),第一個(gè)參數(shù)是獲取一個(gè)令牌桶的時(shí)間間隔,第二個(gè)參數(shù)是重新填裝令牌的時(shí)間(精確到毫秒),第三個(gè)是令牌桶的數(shù)量限制,第四個(gè)是隔多長(zhǎng)時(shí)間重新填裝令牌桶。
-- bucket namelocal key = KEYS[1]-- token generate intervallocal intervalPerPermit = tonumber(ARGV[1])-- grant timestamplocal refillTime = tonumber(ARGV[2])-- limit token countlocal limit = tonumber(ARGV[3])-- ratelimit time periodlocal interval = tonumber(ARGV[4])
local counter = redis.call('hgetall', key)
if table.getn(counter) == 0 then -- first check if bucket not exists, if yes, create a new one with full capacity, then grant access redis.call('hmset', key, 'lastRefillTime', refillTime, 'tokensRemaining', limit - 1) -- expire will save memory redis.call('expire', key, interval) return 1elseif table.getn(counter) == 4 then -- if bucket exists, first we try to refill the token bucket local lastRefillTime, tokensRemaining = tonumber(counter[2]), tonumber(counter[4]) local currentTokens if refillTime > lastRefillTime then -- check if refillTime larger than lastRefillTime. -- if not, it means some other operation later than this call made the call first. -- there is no need to refill the tokens. local intervalSinceLast = refillTime - lastRefillTime if intervalSinceLast > interval then currentTokens = limit redis.call('hset', key, 'lastRefillTime', refillTime) else local grantedTokens = math.floor(intervalSinceLast / intervalPerPermit) if grantedTokens > 0 then -- ajust lastRefillTime, we want shift left the refill time. local padMillis = math.fmod(intervalSinceLast, intervalPerPermit) redis.call('hset', key, 'lastRefillTime', refillTime - padMillis) end currentTokens = math.min(grantedTokens + tokensRemaining, limit) end else -- if not, it means some other operation later than this call made the call first. -- there is no need to refill the tokens. currentTokens = tokensRemaining end
assert(currentTokens >= 0)
if currentTokens == 0 then -- we didn't consume any keys redis.call('hset', key, 'tokensRemaining', currentTokens) return 0 else -- we take 1 token from the bucket redis.call('hset', key, 'tokensRemaining', currentTokens - 1) return 1 endelse error("Size of counter is " .. table.getn(counter) .. ", Should Be 0 or 4.")end
看一下調(diào)用令牌桶l(fā)ua的JAVA代碼,也比較簡(jiǎn)單:
public Boolean distributedRateLimit(String key, String limit, String seconds) { Long id = 0L; long intervalInMills = Long.valueOf(seconds) * 1000; long limitInLong = Long.valueOf(limit); long intervalPerPermit = intervalInMills / limitInLong;// Long refillTime = System.currentTimeMillis();// log.info("調(diào)用redis執(zhí)行l(wèi)ua腳本, {} {} {} {} {}", "ratelimit", intervalPerPermit, refillTime,// limit, intervalInMills); try { id = redisTemplate.execute(rateLimitScript, Collections.singletonList(key), String.valueOf(intervalPerPermit), String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis()), String.valueOf(limitInLong), String.valueOf(intervalInMills)); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("error", e); }
if(id == 0L) { return false; } else { return true; } }
創(chuàng)建兩張簡(jiǎn)單表,一個(gè)庫(kù)存表,一個(gè)是銷(xiāo)售訂單表:
CREATE TABLE `catalog` ( `id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(50) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '名稱(chēng)', `total` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '庫(kù)存', `sold` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '已售', `version` int(11) NULL COMMENT '樂(lè)觀鎖,版本號(hào)', PRIMARY KEY (`id`)) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE TABLE `sales_order` ( `id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `cid` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '庫(kù)存ID', `name` varchar(30) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '商品名稱(chēng)', `create_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '創(chuàng)建時(shí)間', PRIMARY KEY (`id`)) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
基本已經(jīng)準(zhǔn)備完畢,然后啟動(dòng)程序,打開(kāi)swagger(http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html#),執(zhí)行初始化方法initCatalog:
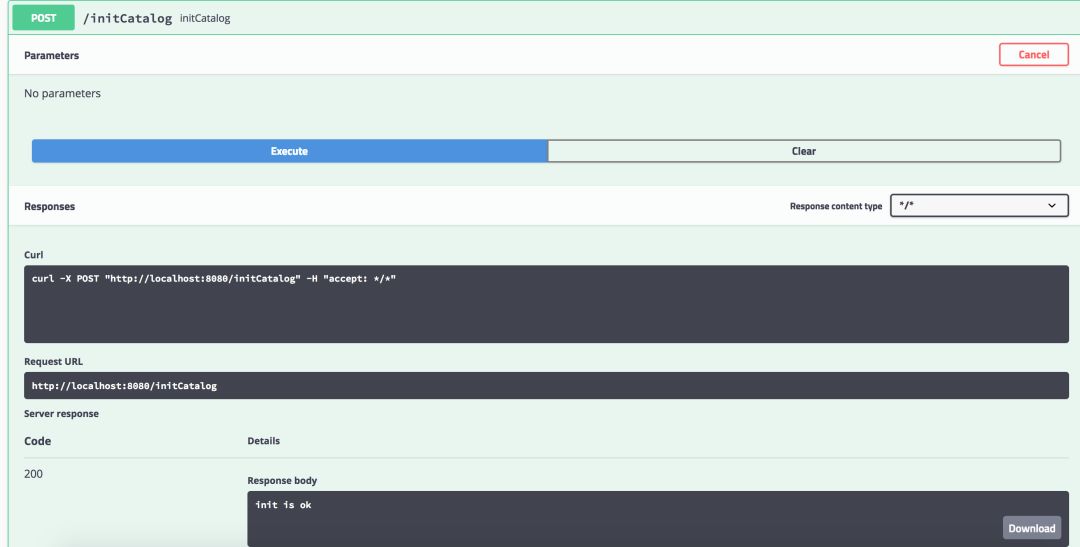
日志里邊會(huì)輸出初始化的記錄內(nèi)容,初始化庫(kù)存為1000:

初始化執(zhí)行的方法,十分簡(jiǎn)單,寫(xiě)到緩存中。
@Override public void initCatalog() { Catalog catalog = new Catalog(); catalog.setName("mac"); catalog.setTotal(1000L); catalog.setSold(0L); catalogMapper.insertCatalog(catalog); log.info("catalog:{}", catalog); redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(CATALOG_TOTAL + catalog.getId(), catalog.getTotal().toString()); redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(CATALOG_SOLD + catalog.getId(), catalog.getSold().toString()); log.info("redis value:{}", redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(CATALOG_TOTAL + catalog.getId())); handleCatalog(); }
我寫(xiě)了一個(gè)測(cè)試類(lèi),啟動(dòng)3000個(gè)線程,然后去進(jìn)行下單請(qǐng)求:
package com.hqs.flashsales;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;import org.junit.Test;import org.junit.runner.RunWith;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;import org.springframework.boot.test.web.client.TestRestTemplate;import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;import org.springframework.util.LinkedMultiValueMap;import org.springframework.util.MultiValueMap;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Slf4j@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)@SpringBootTest(classes = FlashsalesApplication.class, webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)public class FlashSalesApplicationTests {
@Autowired private TestRestTemplate testRestTemplate;
@Test public void flashsaleTest() { String url = "http://localhost:8080/placeOrder"; for(int i = 0; i < 3000; i++) { ? ? ? ? ? ?try { ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20); ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?new Thread(() -> { MultiValueMap
} }
@Test public void contextLoads() { }
}
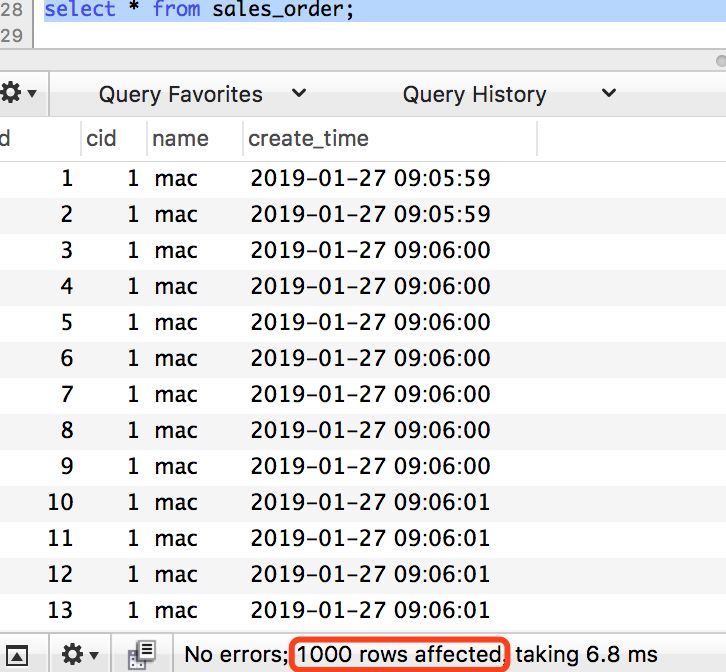
然后開(kāi)始運(yùn)行測(cè)試代碼,查看一下測(cè)試日志和程序日志,均顯示賣(mài)了1000后直接顯示SOLD OUT了。分別看一下日志和數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù):
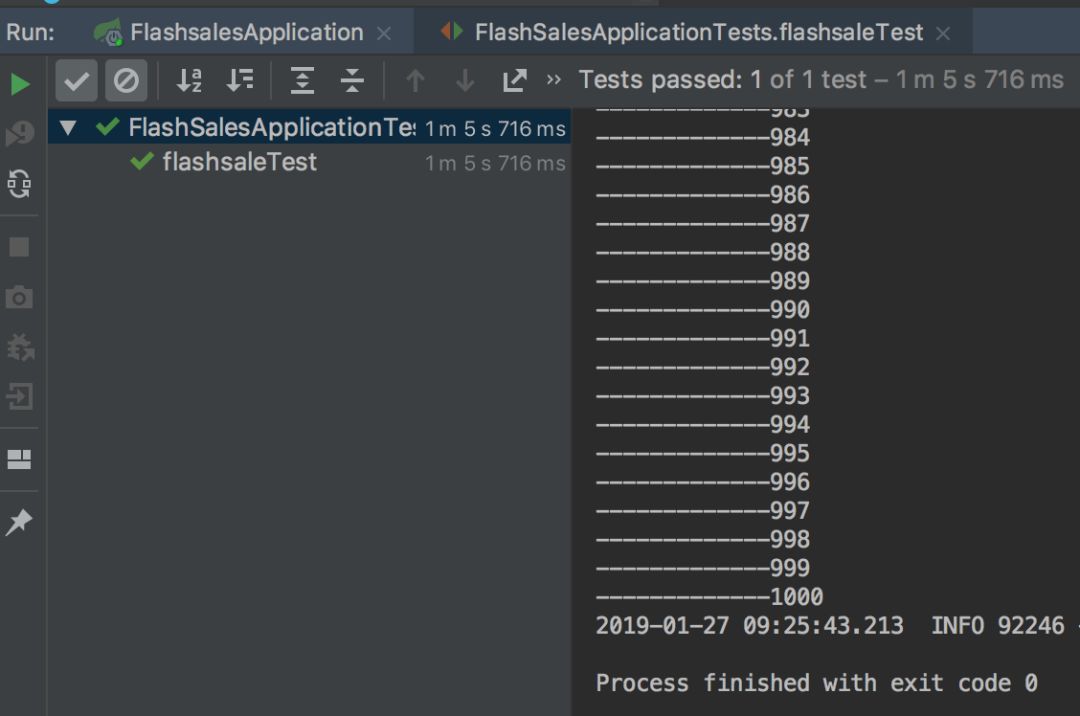
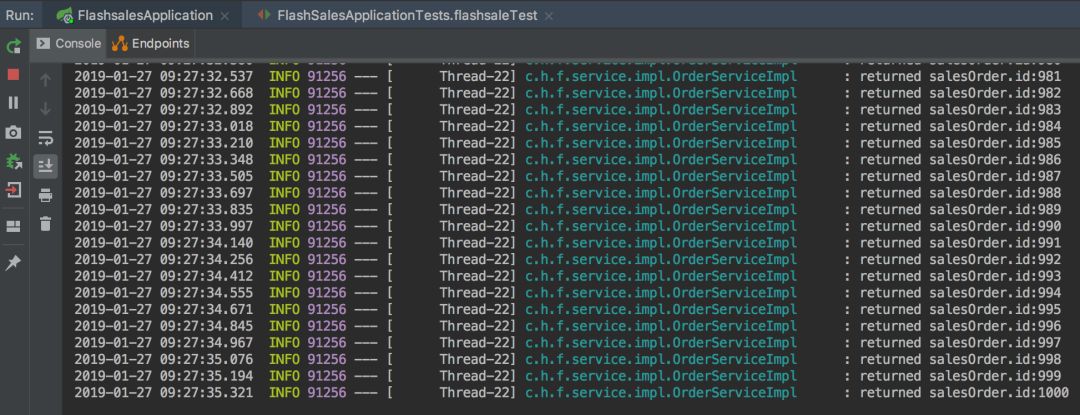
商品庫(kù)存catalog表和訂單明細(xì)表sales_order表,都是1000條,沒(méi)有問(wèn)題。
總結(jié):
通過(guò)采用分布式鎖和分布式限流,即可實(shí)現(xiàn)秒殺流程,當(dāng)然分布式限流也可以用到很多地方,比如限制某些IP在多久時(shí)間訪問(wèn)接口多少次,都可以的。
令牌桶的限流方式使得請(qǐng)求可以得到更加平滑的處理,不至于瞬間把系統(tǒng)達(dá)到最高負(fù)載。在這其中其實(shí)還有一個(gè)小細(xì)節(jié),就是Redis的鎖,單機(jī)情況下沒(méi)有任何問(wèn)題,如果是集群的話需要注意,一個(gè)key被hash到同一個(gè)slot的時(shí)候沒(méi)有問(wèn)題,如果說(shuō)擴(kuò)容或者縮容的話,如果key被hash到不同的slot,程序可能會(huì)出問(wèn)題。
在寫(xiě)代碼的過(guò)程中還出現(xiàn)了一個(gè)小問(wèn)題,就是寫(xiě)controller的方法的時(shí)候,方法一定要聲明成public的,否則自定義的注解用不了,其他service的注解直接變?yōu)榭眨@個(gè)問(wèn)題也是找了很久才找到。
-
接口
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
33文章
8997瀏覽量
153699 -
數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
7文章
3926瀏覽量
66191 -
腳本
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
1文章
398瀏覽量
28453
原文標(biāo)題:用 IDEA 基于SpringBoot2+ mybatis+Redis實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)秒殺系統(tǒng)(附上源碼)
文章出處:【微信號(hào):AndroidPush,微信公眾號(hào):Android編程精選】歡迎添加關(guān)注!文章轉(zhuǎn)載請(qǐng)注明出處。
發(fā)布評(píng)論請(qǐng)先 登錄
何氏手機(jī)維修秒殺絕殺技術(shù)----笫一集漏電故障的秒殺技術(shù)
秒殺到了個(gè)是德 U1242C
【1元秒殺】萬(wàn)用表1元購(gòu),包郵!數(shù)量有限,先到先得~
如何去實(shí)現(xiàn)一種基于SpringMVC的電商高并發(fā)秒殺系統(tǒng)設(shè)計(jì)
一個(gè)嵌入式視頻監(jiān)控系統(tǒng)的設(shè)計(jì)與實(shí)現(xiàn)
秒殺神券雙組合 vivo 618狂歡眾多炸裂福利勁爆來(lái)襲
一篇文章秒殺三道區(qū)間相關(guān)的問(wèn)題

如何實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)微內(nèi)核操作系統(tǒng)的設(shè)計(jì)
解密高并發(fā)業(yè)務(wù)場(chǎng)景下典型的秒殺系統(tǒng)的架構(gòu)
【源碼版】基于SpringMVC的電商高并發(fā)秒殺系統(tǒng)設(shè)計(jì)思路

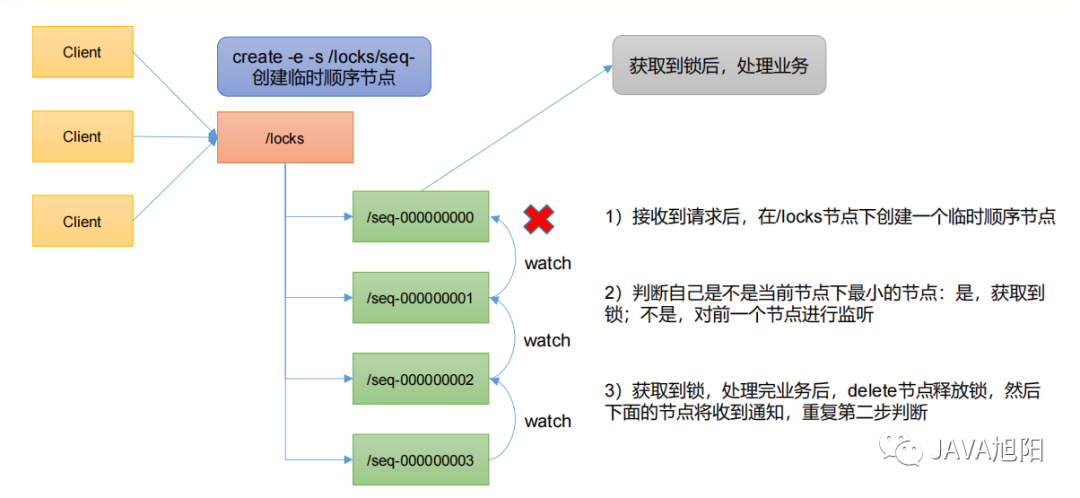
用Zookeeper怎么實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)分布式鎖?
如何控制秒殺商品頁(yè)面購(gòu)買(mǎi)按鈕的點(diǎn)亮
如何實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)malloc





 如何實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)秒殺系統(tǒng)
如何實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)秒殺系統(tǒng)











評(píng)論